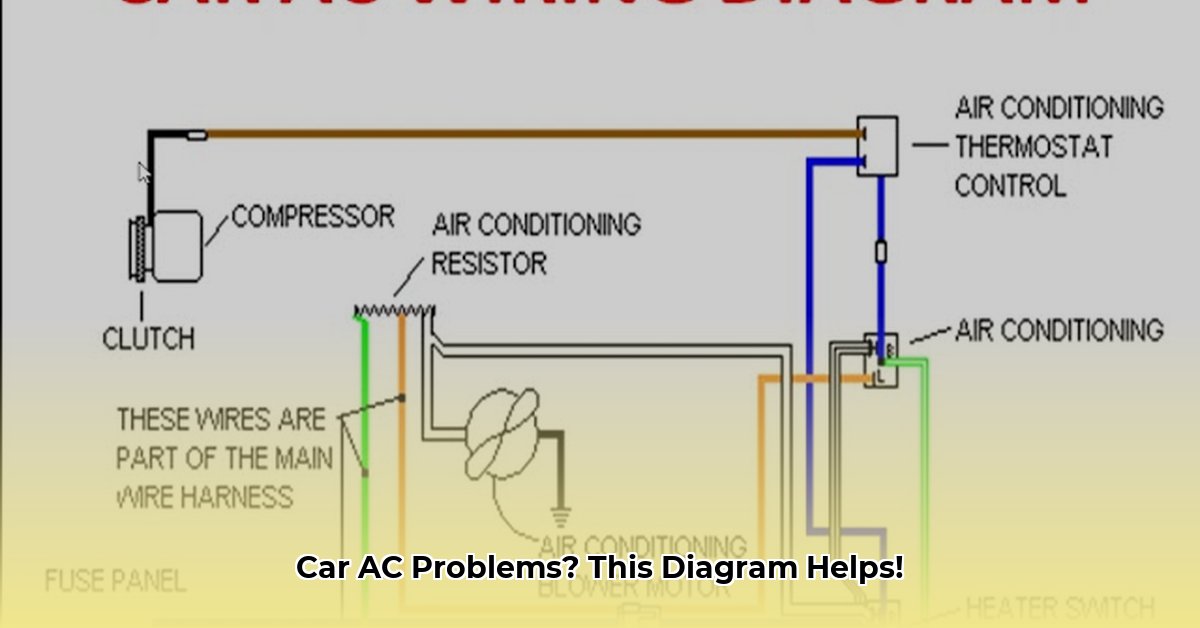
Understanding Your Car’s AC
Your car’s AC system transforms it into a comfortable oasis, but what happens when it starts blowing hot air? This guide decodes your car’s AC system, providing a clear diagram and troubleshooting tips. Whether you’re a car enthusiast or just curious, this guide will empower you to understand and maintain your car’s climate control.
Inside the Cooling System
Your car’s AC is a closed circuit, continuously recycling refrigerant to deliver cool air. Let’s explore this “delivery” route.
The Refrigeration Cycle: A Step-by-Step Journey
-
Compressor: The “heart” of the system, the compressor pressurizes and heats refrigerant gas, much like squeezing a balloon makes the air inside hotter.
-
Condenser: This component, similar to a radiator, cools the hot, high-pressure gas, condensing it back into a high-pressure liquid.
-
Receiver-Dryer/Accumulator: This component acts as a filter and reservoir, removing moisture and storing refrigerant. Systems with a Thermal Expansion Valve (TXV) use a receiver-dryer, while orifice tube systems use an accumulator.
-
Expansion Valve (TXV) or Orifice Tube: These regulate refrigerant flow into the evaporator. A TXV adjusts the flow based on cooling demands, while an orifice tube provides a constant flow.
-
Evaporator: Inside the cabin, the cool liquid refrigerant absorbs heat and evaporates, cooling the air blown over the coils and into your car.
Refrigerant Types: The Evolution of Cool
| Refrigerant | Description |
|---|---|
| R-12 (Freon) | Obsolete due to ozone depletion. |
| R-134a | Being phased out due to high global warming potential. |
| R-1234yf | Current standard with lower global warming potential. |
| Future Refrigerants | Research suggests refrigerants with even lower environmental impact are likely on the horizon. |
Always consult your car’s manual or the sticker under the hood to identify the correct refrigerant.
Basic Troubleshooting
Before rushing to a mechanic, try these simple checks:
- Fuse Check: A blown fuse can disable the entire system. Consult your owner’s manual for the fuse location.
- Belt Inspection: A broken or loose compressor belt prevents the compressor from functioning.
- AC Line Temperature Check: The high-pressure line should be hot, and the low-pressure line should be cold. Similar temperatures may indicate refrigerant flow issues.
Safety Note: Refrigerant is hazardous. Leave complex repairs to qualified technicians.
Delving Deeper
For a more in-depth understanding, consider exploring:
- Thermodynamics: The AC system relies on thermodynamic principles of heat and energy transfer.
- Electrical Components: The AC system incorporates various electrical components for control and operation.
- TXV vs. Orifice Tube: These components manage refrigerant flow and impact system efficiency.
Understanding your car’s AC system empowers you to address minor issues and communicate effectively with mechanics.
Example Diagram (R-134a System)
High-Pressure Side
+-----------------+ +------------+ +-------------------+
| Compressor |----->| Condenser |----->| Receiver-Dryer |
+-----------------+ +------------+ +-------------------+
^ |
| |
| Low-Pressure Side v
+-----------------------------------------+-------------------+
| Expansion Valve (TXV)|
+-------------------+
|
v
+-------------------+
| Evaporator |
+-------------------+
Troubleshooting Tips
-
No Cold Air: Possible causes include low refrigerant (suggesting a leak), a malfunctioning compressor, electrical issues, or a faulty expansion valve/orifice tube. Check for proper system engagement and correct temperature settings.
-
Weak Airflow: This often stems from a clogged cabin air filter or blocked vents. A failing blower motor is another possibility. One often overlooked component is the blend door or its actuator. A malfunction here can result in air that isn’t properly mixed or directed.
-
Unusual Noises: Clicking, whining, or other unusual sounds often indicate failing parts. For instance, a worn compressor clutch can produce a distinct clicking sound. A faulty expansion valve can reduce refrigerant flow and cooling capacity.
-
Leaks: Oily residue around components may indicate leaks, which can cause the entire system to malfunction. Leaks should be addressed promptly by a professional.
-
Unpleasant Odors: Mold or mildew in the evaporator case can cause musty smells, requiring a thorough cleaning.
While these tips are helpful starting points, complicated problems necessitate professional assistance. Prioritize safety. Don’t handle refrigerant yourself; it requires specialized equipment and knowledge. Always consult a qualified technician when in doubt. While basic knowledge empowers you, experienced professionals diagnose and resolve complex issues safely and effectively.
- How to Generate Electricity at Home for Energy Independence - January 31, 2026
- How To Create Free Electricity Using Home Renewable Sources - January 30, 2026
- How to Produce Electricity at Home for Energy Independence - January 29, 2026