Geothermal heating and cooling: harnessing the earth’s energy to create a comfortable and efficient home. This comprehensive guide dives deep into geothermal systems, exploring their functionality, types, costs, benefits, and installation process, helping you decide if this sustainable solution is right for your home.
Geothermal Explained
Geothermal systems, also known as ground-source heat pumps (GHPs), leverage the earth’s stable underground temperature to heat and cool your home. A network of pipes, the ground loop, circulates a fluid underground, absorbing heat in the winter and releasing it in the summer. This exchange creates a highly efficient, renewable alternative to traditional HVAC systems. Think of it as nature’s own thermostat.
Geothermal System Types: Finding Your Perfect Fit
Geothermal systems aren’t one-size-fits-all. The ideal system depends on various factors, including property size, geology, and budget.
-
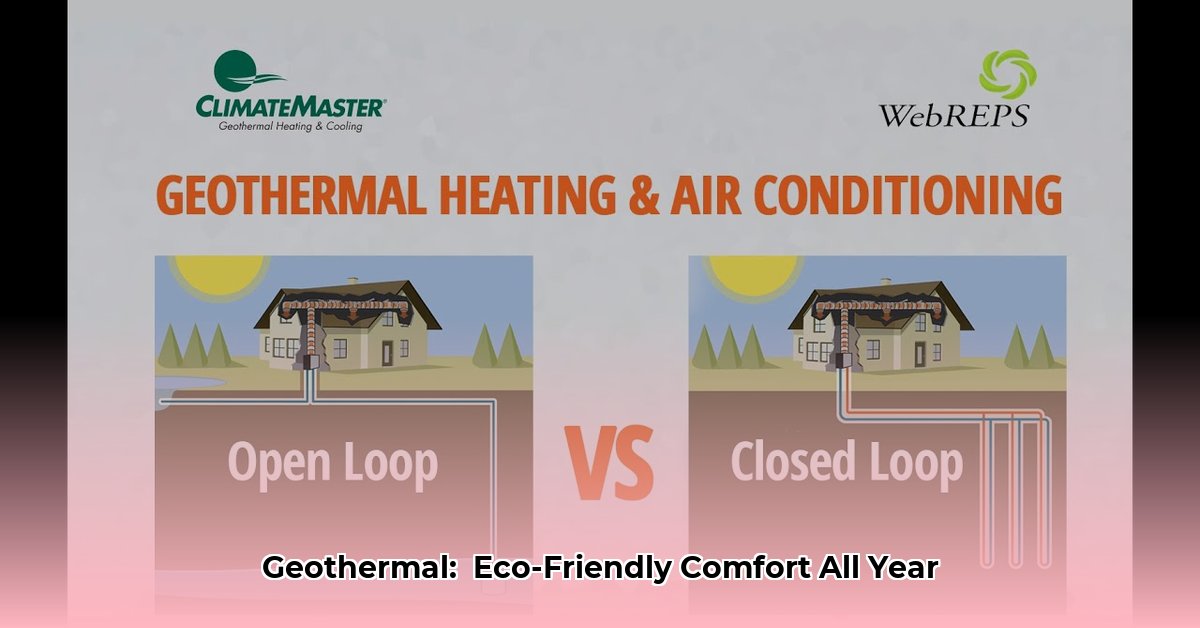
Closed-Loop Systems: These self-contained systems circulate a fluid (typically water and antifreeze) in a continuous loop. Two main subtypes exist:
- Horizontal Loops: Best suited for larger properties, these loops are installed in shallow trenches. Installation is generally less expensive than vertical loops, but requires more land.
- Vertical Loops: Ideal for smaller lots, vertical loops are installed in deep boreholes. While installation is more expensive due to drilling, they are highly efficient and space-saving.
-
Open-Loop Systems: These systems utilize groundwater directly, drawing it from a well, extracting/releasing heat, and then returning it to the source. Requires a suitable water source and adherence to local regulations. Some ongoing research suggests potential long-term impacts on groundwater resources, warranting careful consideration.
-
Direct Exchange (DX) Systems: Highly efficient systems that circulate refrigerant directly through buried copper pipes. Direct heat exchange maximizes efficiency, potentially lowering operating costs. However, installation can be complex, and suitability depends heavily on soil type and climate. Ongoing research aims to improve durability and broaden applicability.
Geothermal Pros and Cons: Weighing the Options
Like any home improvement project, geothermal has its advantages and disadvantages. Careful consideration is key.
Pros:
- Exceptional Energy Savings: Geothermal systems can significantly reduce energy consumption, potentially saving you up to 65% or more on heating and cooling costs compared to conventional systems.
- Environmental Responsibility: Geothermal is a renewable resource, minimizing your carbon footprint and promoting environmental sustainability.
- Longevity: Geothermal systems are built to last, with heat pumps typically lasting 25+ years and ground loops 50+ years.
- Consistent Comfort: Geothermal delivers even heating and cooling, eliminating temperature fluctuations and enhancing home comfort.
- Quiet Operation: Enjoy a peaceful home environment with geothermal’s quiet operation, unlike noisy outdoor AC units.
Cons:
- Higher Initial Investment: Geothermal installation costs are typically higher upfront than traditional HVAC systems. However, long-term energy savings, potential tax incentives, and increased home value can offset this initial expense. Financing options are also available.
- Land Requirements: Horizontal loop systems require substantial land area. Vertical loops are a space-saving alternative, but the drilling process can increase installation costs.
- Installation Disruption: Installation involves digging or drilling, which can temporarily disrupt your landscaping. While inconvenient, it’s a short-term disruption for long-term benefits.
- Site Suitability: Geothermal isn’t suitable for every property. Soil type, groundwater availability, and local climate can influence feasibility. A professional assessment is crucial.
Geothermal vs. Traditional HVAC: A Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | Geothermal | Traditional HVAC |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Very High (up to 65%+ savings) | Moderate |
| Operating Costs | Low | High |
| Lifespan | Long (25+ years heat pump, 50+ loop) | Moderate (15-25 years) |
| Environmental Impact | Low | High |
| Noise Levels | Very Low | Moderate to High |
Geothermal Installation and Maintenance: What to Expect
Geothermal installation is a complex process best handled by qualified professionals. It involves trenching/drilling for the ground loop, connecting it to the indoor heat pump, and integrating with existing ductwork.
Maintenance, however, is minimal. The ground loop requires little attention. Routine maintenance, similar to standard HVAC, focuses on the heat pump unit, including annual checks, filter cleaning, and occasional refrigerant refills.
Geothermal Costs: A Breakdown
Geothermal systems require a higher upfront investment, ranging from $15,000 to $35,000 or more depending on factors like system type, property size, and local labor costs.
| Component | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Ductwork | $2,000 – $6,000 |
| Ground Loop Installation | $5,000 – $15,000 |
| Geothermal Heat Pump | $4,000 – $7,000 |
| Air Handler | $2,000 – $3,000 |
| Permits and Inspections | $100 – $1,000+ |
Financing options, tax credits, and rebates can help offset the initial cost. While the upfront investment is higher, the long-term energy savings and increased home value make geothermal a financially sound choice for many homeowners.
Is Geothermal Right for You?
Determining geothermal’s suitability for your home requires considering your local climate, property conditions, available land, and budget. Consulting with a qualified geothermal installer is essential for a professional assessment, accurate cost estimates, and personalized guidance. They can help you navigate local regulations and permitting requirements.
The Future of Geothermal
Current research focuses on enhancing geothermal efficiency through advanced drilling techniques and innovative heat pump technologies. Hybrid systems combining geothermal with other renewables, like solar, are also being explored. As research progresses, advancements are likely to make geothermal even more accessible and efficient.
Making the Decision
Investing in geothermal is an investment in your home’s comfort, energy efficiency, and environmental sustainability. While the initial cost may seem substantial, the long-term benefits often outweigh the upfront expense. With careful consideration and professional guidance, you can make an informed decision about harnessing the earth’s energy to create a comfortable and eco-friendly home.
- How to Make a Free Energy Source at Home - February 8, 2026
- How Can I Make Free Electricity By Generating Home Power - February 7, 2026
- How To Produce Power At Home Through Alternative Energy Systems - February 6, 2026