Understanding R290
R290, commonly known as propane, is gaining traction as a refrigerant due to its low global warming potential (GWP) and minimal ozone depletion potential. This makes it an environmentally friendly alternative to many synthetic refrigerants. However, its flammability necessitates careful handling and a thorough understanding of its properties, especially the relationship between pressure and temperature. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of R290, its pressure-temperature (PT) characteristics, safe handling procedures, and troubleshooting techniques.
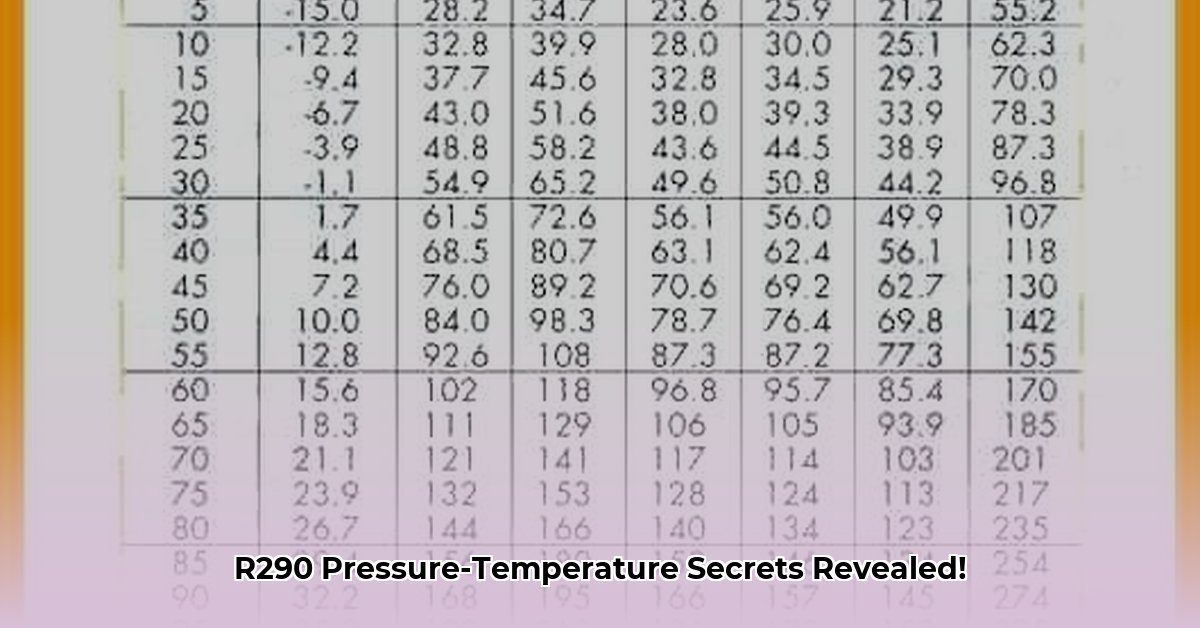
R290 PT Chart Usage
The R290 PT chart, also referred to as a propane PT chart or R290 pressure temperature chart, visually represents the interdependence of pressure and temperature for R290. This chart is an essential tool for HVAC/R technicians, enabling accurate system diagnostics, charge verification, and safe handling of this refrigerant. Understanding the PT relationship is crucial because it helps predict how R290 will behave under different operating conditions. This is particularly important for ensuring efficient system operation and preventing safety issues.
How to Use the R290 PT Chart
-
Safety First: Before interacting with any R290 system, ensure it’s powered off and pressures are equalized to minimize risks associated with its flammability.
-
Temperature or Pressure? Determine whether you have a known temperature or pressure reading from the system.
-
Locate on the Chart: Find the known value on the corresponding axis of the PT chart (temperature in °F or °C, pressure in PSIG or kPa).
-
Cross-Reference: Trace a line horizontally (from temperature) or vertically (from pressure) across the chart until it intersects with the R290 saturation curve.
-
Determine the Corresponding Value: The intersection point reveals the corresponding pressure (if starting with temperature) or temperature (if starting with pressure).
-
Unit Verification: Always double-check that the units on your gauges match the units on the PT chart to avoid misinterpretations.
Example: If your pressure gauge reads 150 psig, find “150” on the pressure axis of the chart. Trace horizontally to the R290 curve. The corresponding temperature at that pressure can then be read from the temperature axis.
Example R290 PT Chart Snippet (Illustrative)
| Temperature (°F) | Pressure (psig) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 19.7 |
| 20 | 31.9 |
| 40 | 47.8 |
| 60 | 67.7 |
| 80 | 92.1 |
| 100 | 121.5 |
A complete, interactive, and downloadable chart will be provided below.
Downloadable R290 PT Chart
Download R290 PT Chart (PDF) [Placeholder – replace with actual link]
(Ensure the PDF includes both °F/°C and psig/kPa scales and is optimized for mobile viewing.)
Key Concepts: Saturation, Superheat, and Subcooling
-
Saturation: The state where R290 can exist as both a liquid and vapor simultaneously. On the PT chart, this is represented by the saturation curve.
-
Superheat: The temperature difference between the refrigerant vapor’s actual temperature and its saturation temperature at a given pressure. Adequate superheat ensures that only vapor enters the compressor, preventing damage. Too low superheat may suggest liquid refrigerant entering the compressor, while excessively high superheat may indicate inefficient operation.
-
Calculating Superheat: Actual Vapor Temperature – Saturation Temperature (at measured pressure)
-
Subcooling: The temperature difference between the refrigerant liquid’s actual temperature and its saturation temperature at a given pressure. Sufficient subcooling ensures that only liquid enters the expansion valve. Inadequate subcooling could lead to two-phase refrigerant entering the valve and affecting system efficiency.
-
Calculating Subcooling: Saturation Temperature (at measured pressure) – Actual Liquid Temperature
Troubleshooting with the R290 PT Chart
The PT chart plays a crucial role in diagnosing system issues. By comparing measured pressures and temperatures with expected values from the chart, technicians can pinpoint the likely source of the problem.
Example Scenarios:
- Low Pressure: Could suggest an undercharge or a leak. Further investigation and consideration of superheat and subcooling values will aid in determining the most probable cause.
- High Pressure: Could indicate an overcharge, a blockage in the system, or air in the system. Again, superheat and subcooling analysis, in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, can pinpoint the culprit.
- Abnormal Superheat/Subcooling: Deviations from expected values can pinpoint issues like metering device problems, faulty expansion valves, or incorrect refrigerant charge.
R290 Safety Precautions
Given R290’s flammability, stringent safety measures are paramount. Always adhere to the following precautions:
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in work areas to disperse any potential leaks.
- Leak Detection: Utilize approved leak detectors designed for flammable refrigerants.
- Equipment: Employ tools and equipment specifically rated for use with flammable refrigerants.
- Storage: Store R290 cylinders upright, in a well-ventilated area, away from ignition sources.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses and gloves, when handling R290.
Regulatory Information and Best Practices
- EPA Regulations: Stay informed about the latest EPA regulations concerning R290 handling, use, and disposal. Consult the EPA website for the most current information.
- ASHRAE Standards: Adhere to relevant ASHRAE standards related to R290 systems, including safety and design guidelines. Visit the ASHRAE website for access to standards and other technical resources.
- Manufacturer Guidelines: Consult equipment manufacturers’ specifications and recommendations for R290-specific systems.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
*(This section will address commonly encountered questions about R290, including its properties, benefits, safe handling practices, and regulatory compliance.)
Glossary of Terms
(Define key HVAC/R terms relevant to understanding and working with R290, including: PSIG, kPa, saturation, superheat, subcooling, GWP, ODP, etc.)
- How to Produce Free Energy for Your Home - February 11, 2026
- How to Generate Electricity for Free at Home - February 10, 2026
- How To Produce Free Electricity By Generating Your Own Power - February 9, 2026

![R410A PT Chart (Pressure-Temperature Chart): Updated [Year] r410a_pt_chart_edited](https://txgenco.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/r410a_pt_chart_edited-150x150.jpg)











