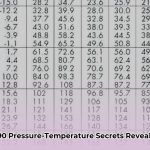
Introduction to R404A and Its PT Chart
R404A is a refrigerant blend commonly used in commercial refrigeration systems, known for its effectiveness at low and medium temperatures. Understanding the relationship between its pressure and temperature is crucial for diagnosing system issues and ensuring optimal performance. This is where the R404A PT (Pressure-Temperature) chart comes in. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of the R404A PT chart, its use, and relevant safety considerations. Whether you’re an HVAC technician, engineer, student, or simply curious, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to interpret the chart effectively.
Understanding the R404A PT Chart
The R404A PT chart visually represents the relationship between the refrigerant’s pressure and temperature. It’s a crucial tool for technicians, enabling them to diagnose system issues and maintain optimal performance. Imagine trying to fix a car without understanding how the engine works—similarly, the PT chart is essential for navigating the complexities of a refrigeration system.
Why Is the PT Chart Important?
The PT chart is indispensable for:
- System Diagnostics: Quickly identify potential problems like leaks, blockages, or compressor issues.
- Refrigerant Charging: Determine the correct refrigerant charge based on system pressures and temperatures.
- Performance Optimization: Fine-tune the system for maximum efficiency and energy savings.
Accessing the R404A PT Chart
While a dynamic chart is ideal for interactive use, a static version is provided below for quick reference. Many online resources offer downloadable PDF versions for convenient access. A quick online search will yield several reputable sources for these charts.
(Insert R404A PT Chart image/PDF here)
How to Use the R404A PT Chart: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Gather Your Tools: You’ll need pressure gauges, a thermometer (for ambient temperature), and your R404A PT chart.
- Connect Gauges: Attach the gauges to the designated service ports on your HVAC system.
- Record Readings: Note both the high-side (discharge) and low-side (suction) pressure readings. Simultaneously, measure the ambient air temperature.
- Consult the Chart: Locate your measured pressure on the chart’s vertical axis. Trace horizontally until you intersect the temperature curve corresponding to your measured ambient temperature.
- Interpret the Results: The intersection point reveals the refrigerant’s saturation temperature. Any significant deviation from expected values indicates a potential problem.
Decoding Superheat and Subcooling
- Superheat: The temperature difference between the refrigerant vapor and its saturation temperature at the same pressure. High superheat may suggest low refrigerant, while low superheat could indicate an overcharge or other issues.
- Subcooling: The temperature difference between the refrigerant liquid and its saturation temperature. Low subcooling can indicate a refrigerant leak or other problems.
Troubleshooting Common HVAC Issues
- Low Suction Pressure: This likely indicates a refrigerant leak, restricted refrigerant flow (possibly a clogged filter-drier), or a malfunctioning metering device.
- High Discharge Pressure: This suggests restricted airflow across the condenser (dirty coils, faulty fan), an overcharge, or non-condensable gases in the system.
- Low Both Pressures: Probably suggests a major refrigerant leak, or a significant compressor malfunction.
- Fluctuating Pressures: This may indicate a faulty compressor, expansion valve issues, or intermittent blockages.
Safety Precautions
Working with refrigerants requires strict adherence to safety regulations.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent oxygen displacement.
- PPE: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (gloves, safety glasses).
- Certified Technicians: Refrigerant handling should be performed by certified technicians. Improper handling can lead to environmental damage and health risks. This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute for professional training and certification.
- Recovery and Recycling: Leaks require proper refrigerant recovery and recycling using EPA-approved equipment. Never release refrigerant directly into the atmosphere.
R404A Phaseout and Alternatives
Due to its high Global Warming Potential (GWP), R404A is being phased out. Alternatives such as R407C, R407F, R448A, and R449A offer lower GWP and similar performance characteristics. Staying informed about these alternatives is crucial for professionals in the HVAC/R industry. Research into even more sustainable options is ongoing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
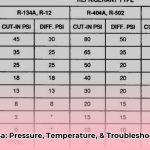
- Q: Where can I find a reliable R404A PT chart?
-
A: Reputable HVAC/R suppliers, industry organizations (like ASHRAE), and online resources often provide accurate charts.
-
Q: What units are used on the PT chart?
- A: Commonly, pressure is in PSI (pounds per square inch) or kPa (kilopascals), and temperature is in degrees Fahrenheit (°F) or Celsius (°C). Ensure your chart uses the correct units for your region.
Glossary of Terms
- Saturation Temperature: The temperature at which a refrigerant changes state (liquid to vapor or vice versa) at a given pressure.
- Superheat: The temperature difference between refrigerant vapor and its saturation temperature.
- Subcooling: The temperature difference between refrigerant liquid and its saturation temperature.
- GWP (Global Warming Potential): A measure of how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere over a specific time, relative to carbon dioxide.
Resources and Further Reading
- ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers)
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) – Search for “refrigerant”
Call to Action
Download a printable R404A PT chart and explore the provided resources to deepen your understanding of refrigerants and HVAC systems. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
- How to Produce Free Energy for Your Home - February 11, 2026
- How to Generate Electricity for Free at Home - February 10, 2026
- How To Produce Free Electricity By Generating Your Own Power - February 9, 2026


![R410A PT Chart (Pressure-Temperature Chart): Updated [Year] r410a_pt_chart_edited](https://txgenco.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/r410a_pt_chart_edited-150x150.jpg)