Worried about fluctuating energy costs and the increasing need for sustainable practices? This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap for leveraging solar power to significantly improve your company’s bottom line from 2025 to 2030. By assessing the latest solar energy options and offering actionable strategies, you’ll be equipped to make informed decisions and secure a sustainable energy future for your business. Discover how to make solar power work for businesses of all sizes, ensuring your company’s future with clean, affordable energy.
Solar Energy for Companies: A Roadmap to Success (2025-2030)
Adopting solar energy for your business is a strategic decision that can significantly enhance your profits. The key lies in understanding the current market landscape, technological advancements, and planning your approach with a long-term perspective.
Understanding the 2025-2030 Solar Energy Landscape and Available Incentives
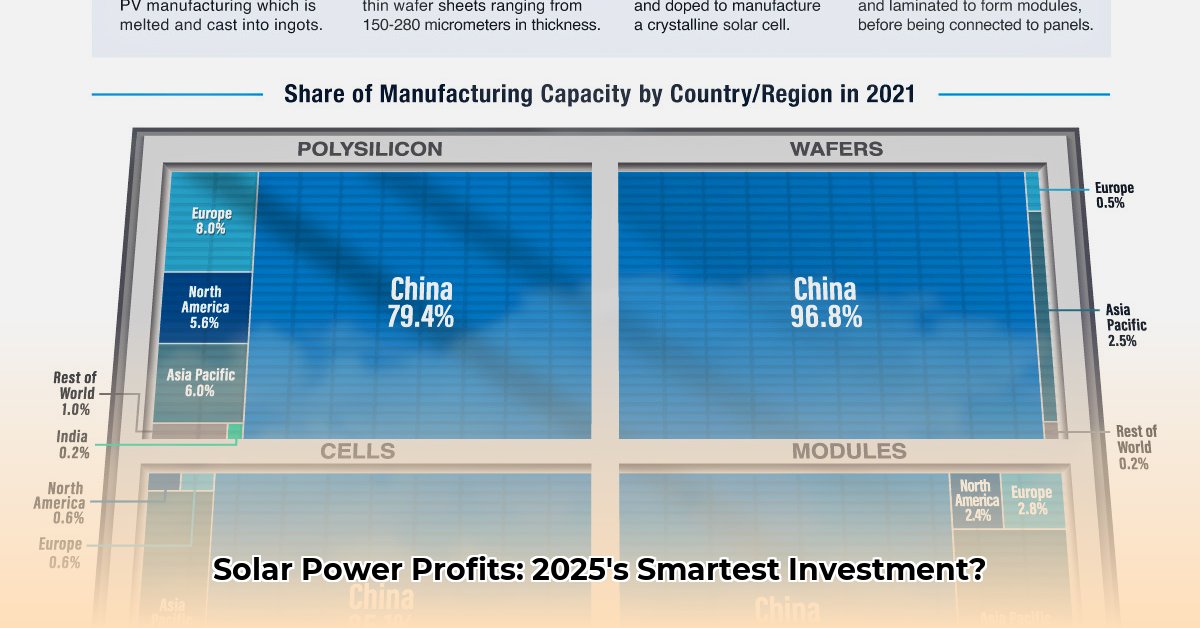
The commercial solar energy market is experiencing considerable growth, driven by decreasing equipment costs, government incentives, and increasing consumer demand for sustainable business practices. Lower electricity bills are a major motivator, attracting numerous businesses to switch to solar power, and a growing segment of customers prefers companies that prioritize environmental sustainability.
Navigating this evolving landscape requires staying informed about key trends:
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in solar panel efficiency, energy storage solutions (like lithium-ion batteries and flow batteries), and smart grid technologies are continuously improving the performance and cost-effectiveness of solar energy systems.
- Policy and Regulatory Changes: Government solar tax credits, rebates, and renewable energy mandates are evolving at both the federal and state levels. Understanding these policies is essential for maximizing savings and ensuring compliance.
- Financing Options: A range of financing options, including Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), solar loans, leases, and community solar programs, are available to businesses of all sizes. Understanding the terms and conditions of each option is crucial for making the right choice.
Is Your Company Ready for Solar? A Readiness Assessment Guide
Before committing to solar energy, a thorough assessment is crucial. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to determine your company’s readiness:
- Energy Audit – Know Your Numbers: Conduct a detailed energy audit to understand your business’s energy consumption patterns, peak demand, and overall energy usage. This baseline data is essential for determining the appropriate size and configuration of your solar system. Consider engaging a certified energy auditor to ensure accuracy and identify opportunities for energy efficiency improvements.
- Site Survey – Does Your Location Work? Evaluate the suitability of your location for solar panel installation. Factors to consider include roof size and orientation (south-facing roofs generally receive the most sunlight), structural integrity (can your roof support the weight of solar panels?), shading from trees and nearby buildings, and local weather conditions. A professional site assessment can confirm whether your building is conducive to solar energy generation and identify any potential challenges.
- Financial Planning – Different Ways to Pay: Explore various financing options, including Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), loans, leases, and self-financing. PPAs offer minimal upfront costs and predictable energy rates, while loans and self-financing provide ownership and potential tax benefits. Compare the long-term financial implications of each option, considering factors such as interest rates, tax incentives, depreciation, and energy savings.
- Choosing the Right Solar Provider – Shop Around! Obtain quotes from multiple reputable solar companies to compare their offerings, warranties, installation expertise, and customer service. Consider factors such as the company’s experience, certifications, insurance coverage, and track record of successful installations. Request references from previous customers and read online reviews to assess their reputation.
- Navigating the Rules – Permits and Regulations: Research and comply with all applicable local regulations, permitting requirements, and interconnection agreements. Engage with local authorities and utility companies to understand the necessary approvals and procedures. Verify that your chosen solar provider handles all necessary permits and approvals to avoid delays and legal complications.
Getting the Most Bang for Your Solar Buck: Maximizing Your Return on Investment (ROI)
To optimize your return on investment from solar energy, consider these critical factors:
- Smart System Design: A well-designed solar system maximizes energy production and minimizes waste. Work with a qualified solar installer to optimize panel placement, system orientation, and energy storage integration. Consider factors such as shading, roof angle, and weather patterns to maximize energy generation.
- Energy Storage – Power When You Need It: Battery storage systems smooth out fluctuations in solar power generation, providing a reliable power source, especially during cloudy days or peak demand. Explore different battery technologies, such as lithium-ion, flow batteries, and solid-state batteries, to determine the best option for your needs. Consider factors such as storage capacity, discharge rate, lifespan, and cost.
- Energy Efficiency – Double Your Savings: Combine solar power with energy-efficient practices and smart technologies to amplify your savings. Conduct an energy audit to identify opportunities for improvement, such as upgrading to LED lighting, installing smart thermostats, sealing windows and doors, and investing in energy-efficient equipment. Implementing energy-efficient practices reduces your overall energy consumption and maximizes the benefits of your solar system.
- Net Metering: Understand your utility company’s net metering policies. Net metering allows you to receive credits on your bill for excess solar energy that you send back to the grid. This can significantly reduce your electricity costs and improve your ROI.
The Upsides and Downsides of Going Solar: Weighing the Pros and Cons
While solar power offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to acknowledge potential drawbacks:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Significantly lower electricity bills and reduced operating costs | High initial costs (mitigated by PPAs) |
| Improved company image and enhanced brand reputation | Site suitability may be a limiting factor (e.g., limited roof space, excessive shading) |
| Potential to sell excess energy back to the grid (net metering) | Navigating permits and regulations can be complex and time-consuming |
| Long-term energy independence and reduced reliance on fossil fuels | Solar power generation is weather-dependent, and energy production may fluctuate depending on sunlight availability |
| Reduced carbon footprint and contribution to a cleaner environment | Solar panel manufacturing and disposal have environmental impacts, though these are being addressed through responsible sourcing and recycling programs |
| Potential eligibility for tax credits, rebates, and other financial incentives | Degradation of solar panel performance over time (typically around 0.5% per year), which may reduce energy production |
| Increased property value and attractiveness to environmentally conscious customers and investors | Electricity rates are not guaranteed to be fixed forever if you choose PPA |
Planning for the Long Haul: A Sustainable Solar Strategy
Develop a long-term vision for solar energy integration. Smaller businesses can integrate solar into their broader sustainability initiatives, such as reducing waste, conserving water, and promoting employee engagement. Larger corporations might explore solar farms, virtual PPAs (VPPAs), or carbon offset programs to meet their significant energy demands and sustainability goals. Regardless of size, continuously monitor your ROI, track your environmental impact, and advocate for supportive renewable energy policies.
The Bottom Line: Solar Power – A Smart Business Move
Adopting solar energy is a strategic move for businesses, it’s environmentally responsible and financially beneficial. By following these guidelines and assessing critical factors, businesses can effectively use solar power to enhance profitability and strengthen sustainability. Ongoing advancements in solar technology mean that staying informed is crucial for making the most of this renewable energy source.
How to Compare Solar Energy PPA vs. Outright Purchase for Small Businesses
Choosing between a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) and outright ownership of a solar energy system can significantly impact your small business. By understanding the key differences and evaluating your specific needs, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Understanding Your Options: PPA vs. Ownership
A PPA involves a long-term contract (typically 10-25 years) where a third party owns, installs, and maintains the solar panels on your property. You purchase the electricity generated at a fixed rate, often lower than standard grid rates. This is similar to leasing solar power. PPAs require little to no upfront investment, making them attractive to businesses with limited capital.
Outright ownership means you purchase and own the entire solar energy system. This option requires a substantial upfront investment but provides long-term financial benefits, including potential tax incentives, depreciation benefits, and asset appreciation. Ownership gives you full control over the system and its performance.
How to Compare: A Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these steps to determine which option best suits your business:
- Assess Your Finances: Determine whether your budget can accommodate the significant upfront cost of outright ownership versus the zero upfront cost of a PPA. Consider your access to capital, borrowing capacity, and investment priorities.
- Evaluate Your Energy Needs: Conduct a detailed energy audit to determine your business’s annual electricity consumption, peak demand, and load profile. This analysis informs your cost calculations for both options and helps determine the appropriate system size.
- Analyze Long-Term Costs: Compare the total cost of energy over the system’s lifespan (typically 25-30 years) for both PPA and ownership options. Consider factors such as the
- How To Make Free Electricity To Run Your Home With Renewable Sources - February 12, 2026
- How to Produce Free Energy for Your Home - February 11, 2026
- How to Generate Electricity for Free at Home - February 10, 2026