So, you’re using testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), and you want to know when those levels are going to be at their highest after a shot? It’s a great question, and the answer isn’t as simple as you might think. This instructional guide will break down the science behind testosterone peaks, explain how different types of testosterone injections work differently, and help you understand what factors influence your personal results. We’ll cover how to monitor your levels effectively, work with your doctor, manage potential side effects, and even look at what’s coming next in TRT research. Let’s get you the information you need to make the most of your TRT.
When Does Testosterone Peak After Injection? Understanding TRT Timing
So, you’re considering testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) and want to know when you’ll feel the effects? Understanding when testosterone peaks after an injection isn’t a simple “one-size-fits-all” answer, as individual responses can vary significantly. It’s a journey, and this guide will help you navigate it, providing actionable insights into optimizing your TRT experience for health benefits.
Understanding the Different Types of Testosterone: It’s All in the Ester & Hormone Delivery
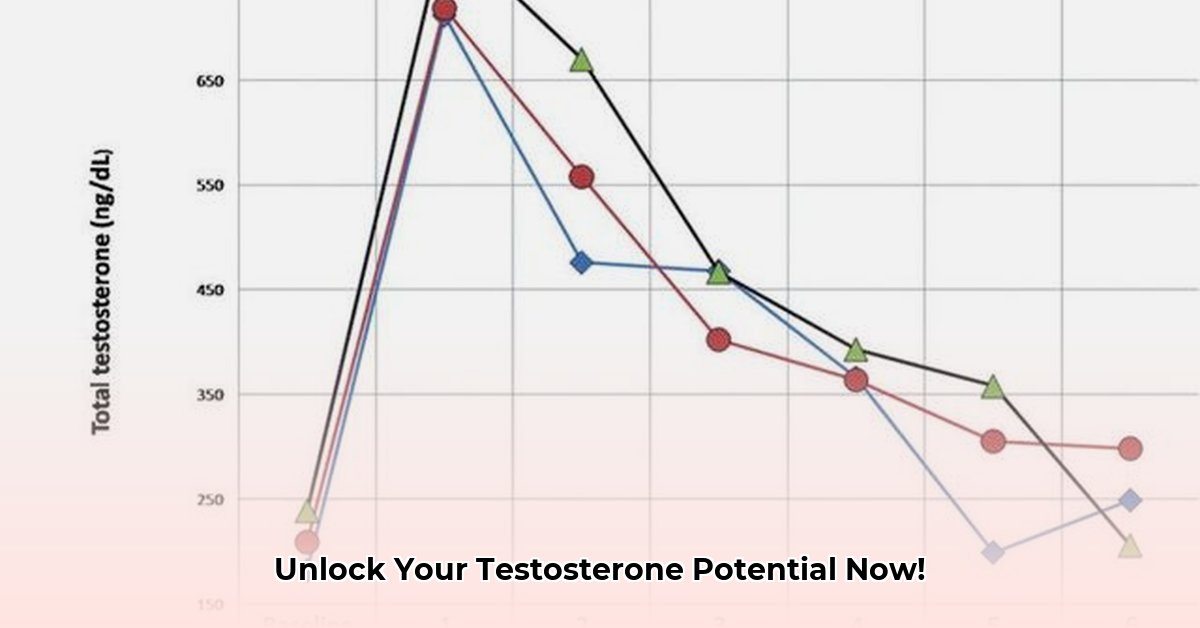
Think of testosterone esters as different delivery systems for your testosterone (a crucial hormone for men’s health). They’re like time-release capsules – some release their payload quickly, while others release it more gradually. This affects how quickly your testosterone levels rise and how long they stay elevated, influencing energy levels and overall well-being. Let’s break down the most common types, examining their unique properties:
| Ester Type | Peak Time Range (Hours) | What to Expect | Injection Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propionate | 2-6 | Fast-acting, but the effect doesn’t last as long, so requires more frequent injections | Every 1-3 days |
| Enanthate | 24-72 | Slower to kick in, but provides a longer boost, offering more stable levels | Every 1-2 weeks |
| Cypionate | 24-72 | Similar to enanthate, potentially a bit longer, also providing stable levels | Every 1-2 weeks |
| Undecanoate | 5-14 days | Very slow release, providing sustained testosterone levels with less frequent injections | Every 10-14 weeks |
Propionate is like a short burst of energy – a quick rise and fall in testosterone levels. Enanthate and cypionate are more of a marathon, offering a steadier increase over time and maintaining those higher levels for longer. Undecanoate provides the slowest release, requiring the fewest injections. Your doctor will recommend the best type for your individual needs and health goals, considering factors like desired stability and convenience.
It’s Not Just the Injection: Your Body Plays a Big Role in Peak Testosterone Levels
Your body’s unique chemistry significantly impacts when and how intensely you feel the effects of your testosterone injection. A few key players here are your metabolism (how quickly your body processes things), and your levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). SHBG is a protein that binds to testosterone, making it less readily available for your body to use. Higher SHBG means less free testosterone floating around, directly impacting how you feel. Other factors that can influence testosterone levels include age, weight, diet, exercise, and underlying health conditions.
Beyond your body’s natural processes, how the injection is administered matters. A deeper intramuscular injection might result in slower absorption of the testosterone compared to a subcutaneous injection, delaying the peak. And finally, dosage is key! A higher dose will likely lead to a more significant and possibly quicker rise in levels, while a lower dose may result in a less pronounced peak, but a longer, more sustained elevation. This comprehensive understanding prepares you for focused instruction.
Working with Your Doctor: Monitoring Your Testosterone Levels and Treatment Plan
Regular blood tests are crucial for optimizing your TRT. This isn’t a one-time thing; it’s an ongoing partnership with your healthcare provider. They’ll use these tests to fine-tune your treatment plan based on your unique response, ensuring optimal hormone balance. To ensure you’re getting the most out of your appointments, here are some questions to ask your doctor:
- How often should I get my blood tested to track my testosterone after injection, considering the ester type and my SHBG levels?
- What are the ideal testosterone levels for me to aim for, considering my symptoms, age, and health goals? Should we be monitoring both total and free testosterone?
- What side effects should I watch out for, and what should I do if they occur, like acne, mood changes, or increased red blood cell count?
- How will we adjust my dosage or injection schedule based on my blood test results, and what specific metrics will we use to guide those changes (e.g., total testosterone, free testosterone, estradiol)?
- What is your experience in managing TRT, and what strategies do you recommend for maximizing benefits and minimizing potential risks?
- Are there any lifestyle modifications, such as diet or exercise, that I can implement to further optimize my TRT?
Remember, open communication is key. Don’t hesitate to express any concerns or questions. Your doctor should be your partner in this process, helping you understand your body’s response and make informed decisions.
What to Expect, and What to Watch Out For: Managing Your TRT and Injection Side Effects
It’s essential to manage expectations. While we can pinpoint general timeframes for testosterone peaks, individual experiences vary, and there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. It may take time and some adjustments to achieve optimal levels, and it’s crucial to have patience.
Be aware that some common side effects can include acne, changes in mood such as increased aggression or anxiety, oily skin, hair loss, and water retention. In rare cases, more serious side effects like sleep apnea, enlarged prostate, and increased risk of blood clots can occur. Keeping an open line of communication with your doctor is vital to address these quickly, and to ensure you’re adjusting your treatment plan accordingly. Don’t hesitate to report any new or concerning symptoms.
To minimize the risk of side effects:
- Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments and blood tests.
- Monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption and smoking.
The Ongoing Journey of Research and Understanding TRT
The field of testosterone replacement therapy is constantly evolving. More research is needed to fully unravel the intricate interplay of factors like SHBG, injection technique, dosage, and individual metabolic differences. Scientists are investigating the optimal dosing strategies, the best ways to administer testosterone (including gels, creams, and pellets), and how your body’s unique characteristics influence the results. Areas of ongoing research include:
- The impact of TRT on cardiovascular health: Studies are exploring the potential risks and benefits of TRT on heart health.
- The role of TRT in cognitive function: Researchers are investigating the effects of TRT on memory, focus, and overall cognitive performance.
- The development of new TRT formulations: Scientists are working on developing new and improved TRT options with fewer side effects and more consistent results.
- Personalized TRT approaches: Research is focused on tailoring TRT to individual needs based on genetic factors, lifestyle, and other health conditions.
This means that our understanding will likely continue to evolve over time! Stay informed, communicate openly with your doctor, and remember that ongoing monitoring is essential for successful, long-term management of your TRT.
Key Takeaways:
- Testosterone ester type significantly impacts peak levels; shorter-acting esters peak faster than longer-acting ones.
- Individual metabolism and SHBG levels influence peak times and injection frequency, demanding personalized approaches.
- Consistent monitoring via blood tests is crucial for personalized TRT optimization, ensuring your safety and effectiveness.
- Open communication with your doctor and awareness of potential side effects are essential for a positive TRT experience.
- The field of TRT is continually evolving, so stay informed and be proactive in your treatment.
How to optimize TRT injection timing based on SHBG levels and individual factors
Understanding the interplay between SHBG (sex hormone-binding globulin) levels and TRT injection timing is vital for optimizing your treatment, maximizing its effectiveness and minimizing potential side effects. This requires a personalized approach that considers your unique physiological profile.
Understanding Testosterone Esters and Their Impact on Hormone Release
Different testosterone esters affect how quickly your levels rise after an injection. Think of it like this: short-acting esters are like a quick burst of energy, while long-acting ones are a slow, steady release of hormones, promoting stable testosterone levels. Here’s a simplified overview:
| Ester Type | Peak Time Range (Approximate) | Notes | Injection Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propionate | 24-48 hours | Fastest-acting; requires more frequent injections to maintain hormonal balance. | EOD to 3x/week |
| Cypionate | 48-72 hours | Commonly used; provides a relatively stable level over several days. | Every 1-2 weeks |
| Enanthate | 72-144 hours | Longer acting than cypionate, requiring less frequent injections for convenience. | Every 1-2 weeks |
- How to Produce Electricity at Home for Energy Independence - January 29, 2026
- How To Create Electricity At Home For Energy Independence - January 28, 2026
- How to Make Electricity at Home Using Renewable Energy Sources - January 27, 2026