Untuk gambaran yang lebih besar dan konteks penuh, pastikan Anda membaca panduan utama kami tentang Wind Energy Powered Cars: Are They the Future of Driving?.
Imagine a world where your car refuels itself as you drive, silently sipping energy from the wind. That’s the promise of the wind energy vehicle, a concept pushing the boundaries of sustainable transportation. While a fully wind-powered car might still seem like science fiction, advancements are being made that bring this technology closer to reality.
At a glance:
- Understand the core technologies that make a wind energy vehicle possible.
- Examine the real-world environmental and economic benefits
- Weigh the current obstacles to widespread adoption.
- Explore the exciting innovations on the horizon for turning wind into transportation fuel.
- Learn about hands-on ways to explore wind energy with kids and adults.
How Does a Wind Energy Vehicle Actually Work?
The basic idea behind a wind energy vehicle is simple: capture the kinetic energy of the wind and convert it into power to propel a car. However, the execution is far more complex. Here’s a breakdown of the core components and processes:
- Kinetic Energy Capture: Wind flows over turbine blades, converting wind speed into rotational motion. The design and placement of those blades are crucial.
- Mechanical Conversion: The rotating blades spin a generator, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Electrical Generation: The generator produces electricity, which is then used to power the car’s motor or stored in a battery.
- Power Delivery: The electricity powers an electric motor, which turns the wheels and propels the car.
Many designs are more hybrid, utilizing wind energy to supplement existing electric or even conventional engines. The placement of the turbine is key, with external placement generally proving more effective than internal designs, allowing it to benefit from a greater volume of airflow.
The Environmental Promise: Cleaner Air and Lower Emissions
One of the most compelling arguments for wind energy vehicles is their potential to significantly reduce our environmental impact. Unlike gasoline-powered cars that spew harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, wind powered cars tap a renewable resource. This directly translates to:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Wind-powered cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, helping to combat climate change.
- Decreased Dependence on Fossil Fuels: Shifting away from gasoline reduces our reliance on a finite and polluting resource.
- Improved Air Quality: Less pollution leads to cleaner air, benefiting public health, especially in urban areas.
But what about the entire lifecycle? Manufacturing wind turbines and batteries does have an environmental footprint. The key is that wind energy vehicles offer a net reduction in emissions compared to traditional vehicles, especially when considering the long-term impact of burning fossil fuels. As manufacturing processes become more sustainable, this advantage will only grow. Could wind power cars? Innovations in sustainable manufacturing, transportation, and recycling offer substantial future benefits for the environment and economy.
Real-World Examples: Prototypes and Pioneering Designs
While mass-produced wind energy vehicles aren’t yet available, several innovative projects demonstrate the possibilities:
- Ventomobile: This early prototype, built by German students, featured a large, two-meter wind turbine mounted on top of a three-wheeled vehicle. It was designed to run solely on wind energy.
- Tang Zhengping’s Creation: A 90-year-old inventor in China built an environmentally friendly car with a front-mounted fan for power generation, supplemented by solar panels. It reached speeds of up to 90 mph.
- Mercedes-Benz Formula Zero: This concept car, though not strictly wind-powered, incorporates aerodynamic features designed for energy efficiency, aiming to utilize natural resources in racing.
Even companies like Lotus are exploring wind power, integrating it into their factory to power car-building machinery. These examples, while diverse, showcase the potential of wind energy to contribute to automotive design and sustainability.
What About the Cost? A Look at the Economic Factors
The economic viability of wind energy vehicles is a complex equation involving several factors:
- Initial Investment: The upfront cost of developing and manufacturing wind-powered cars could be higher than traditional vehicles, due to specialized components and innovative technologies.
- Operational Costs: Wind energy is a free resource, so running costs could be significantly lower than gasoline-powered cars.
- Government Incentives: Tax credits, subsidies, and other incentives can make wind energy vehicles more affordable for consumers.
- Long-Term Savings: Reduced fuel costs and lower maintenance requirements can lead to significant savings over the vehicle’s lifespan.
Furthermore, the growth of the wind energy vehicle industry could create new jobs in manufacturing, engineering, and maintenance, boosting the economy.
The Challenges: Obstacles to Overcome
Despite the potential benefits, wind energy vehicles face several challenges that need to be addressed before they can become a mainstream transportation option:
- Energy Efficiency: Wind energy is intermittent, and the amount of power generated can vary greatly depending on wind conditions.
- Turbine Size and Placement: Integrating a large enough turbine to generate meaningful power without compromising aerodynamics or vehicle design is a significant challenge.
- Energy Storage: Efficient and lightweight battery technology is crucial for storing wind energy and providing a consistent power supply.
- Infrastructure: A lack of charging stations and specialized maintenance facilities could hinder adoption.
- Public Perception: Overcoming skepticism and convincing consumers that wind energy vehicles are a viable option will require education and demonstration of real-world performance.
The Path Forward: Innovations on the Horizon
Researchers and engineers are actively working to overcome these challenges through various innovations:
- Improved Turbine Efficiency: New turbine designs are more efficient at capturing wind energy, even in low-wind conditions.
- Lighter Materials: Carbon fiber and other lightweight materials reduce the energy required to move the vehicle, improving efficiency.
- Integration with Other Energy Sources: Hybrid systems combining wind energy with solar power or battery-electric systems can provide a more reliable and consistent power supply.
- Enhanced Storage Systems: Advanced battery technologies are increasing energy density and reducing weight, allowing for longer driving ranges.
- Aerodynamic Design: Streamlined vehicle designs minimize air resistance, maximizing energy efficiency.
For example, some designs explore integrating small wind turbines within the car itself to generate energy on the move. Other research focuses on kite technology to harness stronger winds at higher altitudes.
Q&A: Addressing Common Questions and Misconceptions
- Q: Will wind-powered cars only work on windy days?
- A: Not necessarily. While windy conditions are ideal, wind energy vehicles can store energy in batteries for use when the wind is calm. Hybrid systems can also supplement wind power with other energy sources.
- Q: Are wind turbines on cars noisy?
- A: Early prototypes were noisy, but advancements in turbine design are significantly reducing noise levels. Future models will likely incorporate noise-reduction features.
- Q: Are wind-powered cars safe?
- A: Safety is a top priority in vehicle design. Wind-powered cars will need to meet the same rigorous safety standards as traditional vehicles. The placement and integration of wind turbines will be carefully engineered to ensure safety.
Practical Playbook: What You Can Do Now
While you can’t buy a wind-powered car just yet, there are several ways to explore wind energy and its potential:
- Build a Mini Wind Turbine: A hands-on project using simple materials like paper, straws, and a small generator can illustrate the principles of wind energy.
- Explore Online Resources: Websites like Wikipedia and Britannica offer extensive information about renewable energy and wind power.
- Visit a Wind Farm: Seeing large-scale wind turbines in action can provide a better understanding of how wind energy is harnessed.
- Advocate for Renewable Energy: Support policies and initiatives that promote the development and adoption of wind energy and other renewable resources.
- Learn About Electric Vehicles: Familiarize yourself with the current state of electric vehicle technology, as it forms a crucial foundation for wind energy vehicles.
Takeaways: A Decision Tree for the Future
Are wind energy vehicles the future of driving? The answer is likely a qualified “yes,” but the path to widespread adoption is complex. Here’s a decision tree to consider:
- Is climate change a pressing concern? If yes, proceed. If no, wind energy vehicles may not be a priority.
- Are you willing to embrace new technologies and designs? If yes, proceed. If no, stick with conventional vehicles for now.
- Are you comfortable with intermittent energy sources? If yes, proceed. If no, consider hybrid systems or alternative renewable energy options.
- Are you willing to invest in a potentially higher upfront cost for long-term savings and environmental benefits? If yes, wind energy vehicles may be a good fit for you in the future.
The journey toward wind-powered transportation is just beginning, but the potential rewards are significant. By embracing innovation, supporting research and development, and educating ourselves about the possibilities, we can help pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable future on the road.

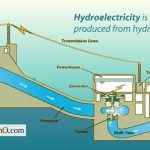
- Is Hydropower Renewable Or Nonrenewable Resource? Sorting Out the Facts - March 3, 2026
- Hydroelectric Power Basics How Water Is Used For Electricity - February 26, 2026
- Portable Water Generators Power Off-Grid Homes and Adventures - February 25, 2026