Newborn jaundice is a common concern, making accurate bilirubin level monitoring essential. For more hospital bilirubinometer options, see this page. This review compares two leading monitors, BiliCare and Dräger JM-105, to help healthcare providers choose the optimal device for their needs. We will analyze their features, usability, accuracy, cost, and overall impact from the perspectives of hospitals, clinicians, regulatory bodies, and manufacturers, enabling informed decisions and enhanced neonatal care.
Hospital-Grade Bilirubin Monitors: A Detailed Comparison of Jaundice Detection Technologies
Newborn jaundice, characterized by elevated bilirubin levels, requires timely and accurate diagnosis. While traditional blood tests can be uncomfortable for newborns, non-invasive transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) monitors offer a gentler and more efficient alternative. These devices measure bilirubin levels through the skin, providing rapid assessments and minimizing discomfort. We delve into two prominent TcB monitors, BiliCare and Dräger JM-105, exploring their features, benefits, and limitations in bilirubin level assessment.
BiliCare: In-Depth Analysis of Features and Benefits
BiliCare is a TcB monitor recognized for its user-friendly design and comprehensive software suite designed to simplify neonatal jaundice screening. It delivers swift bilirubin readings, assisting clinicians in making prompt decisions regarding jaundice management. The device’s software generates detailed reports complemented by graphs and data that facilitate easy storage and seamless transfer to other systems. A significant drawback is that BiliCare is not yet FDA-approved in the United States. The absence of FDA approval poses a substantial challenge for US hospitals considering its adoption. The lack of FDA approval may limit its use in US hospitals and could affect decisions regarding its adoption, impacting neonatal care.
Dräger JM-105: Exploring Features and Cost-Effectiveness
The Dräger JM-105 stands out as another reputable option in the TcB monitor market, acclaimed for its effectiveness in jaundice detection. Its standout features include straightforward operation and an easily cleaned reusable probe, which enhances usability in neonatal settings. A convenient built-in flagging system alerts clinicians to infants who may require closer attention. Cost-effectiveness is frequently highlighted as an advantage, stemming from the reusable probe design. However, comprehensive data on long-term maintenance costs is not widely available. Gaining a holistic understanding of its cost-effectiveness over time necessitates further investigation. While the manufacturer emphasizes ease of use and reduced blood draws, the information regarding the FDA approval status for the Dräger JM-105 remains unclear on the manufacturer’s website. This ambiguity complicates a thorough evaluation of its suitability for use in US hospitals, prompting meticulous consideration of regulatory compliance and device performance.
Head-to-Head: Key Differences and Similarities in Bilirubin Measurement
The following comparison highlights key distinctions and commonalities between the two monitors, providing a clear overview of their strengths and weaknesses in neonatal bilirubin screening:
| Feature | BiliCare | Dräger JM-105 |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Speed | Very fast; provides immediate results. | Very fast; delivers rapid measurements. |
| Method | Non-invasive; minimizes infant discomfort. | Non-invasive; ensures gentle assessment. |
| Data Handling | Generates detailed reports with exportable graphs and data. | Features built-in alerts; data handling methodology requires clarification. |
| Probe Type | Offers choices for both reusable and disposable probe covers. | Reusable probe; reduces disposable costs. |
| FDA Approval (USA) | Not yet approved; restricts use in some US facilities. | Approval status unclear; requires verification for US compliance. |
| Hospital Information System (HIS) Integration | Likely possible via HL7; specific integration details not stated. | Integration method unspecified; requires more detailed investigation. |
| Calibration Requirements | LEDs do not require calibration, minimizing maintenance costs. | Requires regular calibration to ensure accuracy. |
| Display | Unique software displays results in tables and graphs. | Easy-to-read LCD screen. |
| Special Features | Can switch to “Large Numbers” display for better visibility. | Integrated flagging feature to track patients needing special attention. |
Choosing the Right Monitor: Perspectives from Different Angles for Neonatal Care
The optimal monitor choice hinges on the specific needs and priorities of the hospital and its staff, which in turn impacts jaundice treatment protocols. Hospitals may emphasize affordability and ease of integration with existing systems, whereas clinicians might prioritize user-friendliness, measurement speed, and the clarity of results interpretation. Regulatory agencies naturally place the highest importance on FDA approval and adherence to stringent safety standards. Manufacturers, on the other hand, bear the responsibility of addressing any limitations and furnishing transparent, comprehensive information about their respective medical devices. It’s also crucial to factor in long-term costs, such as maintenance and the procurement of replacement probes, when evaluating these monitors to enhance patient outcome.
Managing Potential Risks: A Safety-First Approach to Jaundice Measurement
Introducing any new medical technology brings inherent risks. In the context of TcB monitors, potential risks encompass inaccuracies in readings, challenges in seamlessly integrating with existing hospital systems, and concerns regarding regulatory compliance, all of which could compromise patient safety. To mitigate these risks, comprehensive testing is paramount. This entails rigorous data validation, the establishment of robust service contracts, and unwavering adherence to stringent quality control procedures, reinforcing the paramount importance of accuracy and reliability.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: The FDA and Beyond for Medical Devices
The absence of clear FDA approval for both monitors presents a hurdle to their widespread adoption in US healthcare facilities. Manufacturers must conduct thorough clinical trials to demonstrate the accuracy and safety of their devices, fulfilling the FDA’s rigorous requirements for approval. This pivotal step is essential for ensuring these monitors become readily available in US hospitals, meeting the indispensable healthcare standards demanded.
The Bigger Picture: Ongoing Research and Future Directions in Neonatal Monitoring
The field of neonatal jaundice detection is dynamic and continually evolving. Ongoing research may uncover further benefits and limitations associated with these monitors, potentially reshaping our understanding of their effectiveness and appropriateness, and influencing future treatment strategies. Staying abreast of the latest research findings and technological advancements is imperative to ensure the delivery of optimal care to newborns. Future advancements could lead to improved accuracy, enhanced integration with hospital systems, and even more intuitive user interfaces, thereby amplifying the devices’ effectiveness and ease of integration into hospital workflows.
How to Choose Between BiliCare and Dräger JM-105 for Neonatal Jaundice Screening
Key Takeaways:
- Transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) measurement offers a faster, less invasive alternative to traditional blood tests in jaundice screening.
- While TcB provides a valuable estimate, it’s crucial to recognize that TcB readings may not always perfectly align with total serum bilirubin (TSB) and care should be taken during assessment.
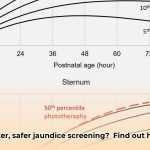
- The Dräger JM-105 aligns with American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines for infants over 35 weeks gestation, promoting standardized care.
- The choice between the BiliCare and Dräger JM-105 hinges on hospital needs, budget, integration capabilities, and the specific clinical context.
Understanding Transcutaneous Bilirubin (TcB) Measurement for Neonatal Jaundice
Neonatal jaundice, a common occurrence in newborns, demands prompt and accurate assessment of bilirubin levels to ensure effective management. Traditional methodologies, often involving blood draws, can cause discomfort for infants and introduce delays in obtaining results. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry (TcB), facilitated by devices such as the Dräger JM-105 and BiliCare, furnishes a non-invasive alternative for bilirubin level assessment. These devices quantify bilirubin levels through the skin, yielding rapid results and mitigating the need for invasive procedures. But is this new method effective in clinical practice? Let’s explore this and understand its role in neonatal care.
Dräger JM-105: A Closer Look for Accurate Bilirubin Readings
The Dräger JM-105 leverages TcB technology to aid in jaundice detection. Engineered for swift, non-invasive bilirubin assessments in newborns, it fosters improved patient outcomes while minimizing stress for both infants and caregivers. The reusable probe design contributes to cost savings, enhancing its appeal in resource management. The device demonstrates a favorable correlation with TSB levels. However, it may underestimate TSB levels, a factor that warrants consideration when formulating treatment plans.
BiliCare: Features and Considerations in Bilirubin Measurement
BiliCare presents a distinct approach to TcB measurement. Investigating aspects such as the cost per test, user-friendliness, and integration capabilities with hospital systems is imperative when gauging its effectiveness. How does its ease of use compare to the Dräger JM-105, and how does it factor into the decision-making process?
Comparing the Contenders: JM-105 vs. BiliCare for Effective Monitoring
To facilitate the selection of the most suitable device, consider the following factors that influence the effectiveness of jaundice monitoring:
| Feature | Dräger JM-105 | BiliCare |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Method | Transcutaneous Bilirubin (TcB) | Transcutaneous Bilirubin ( |
- How To Produce Power At Home Through Alternative Energy Systems - February 6, 2026
- How Can I Make Electricity At Home Using Renewable Energy? - February 5, 2026
- How To Generate Power At Home For Energy Independence - February 4, 2026