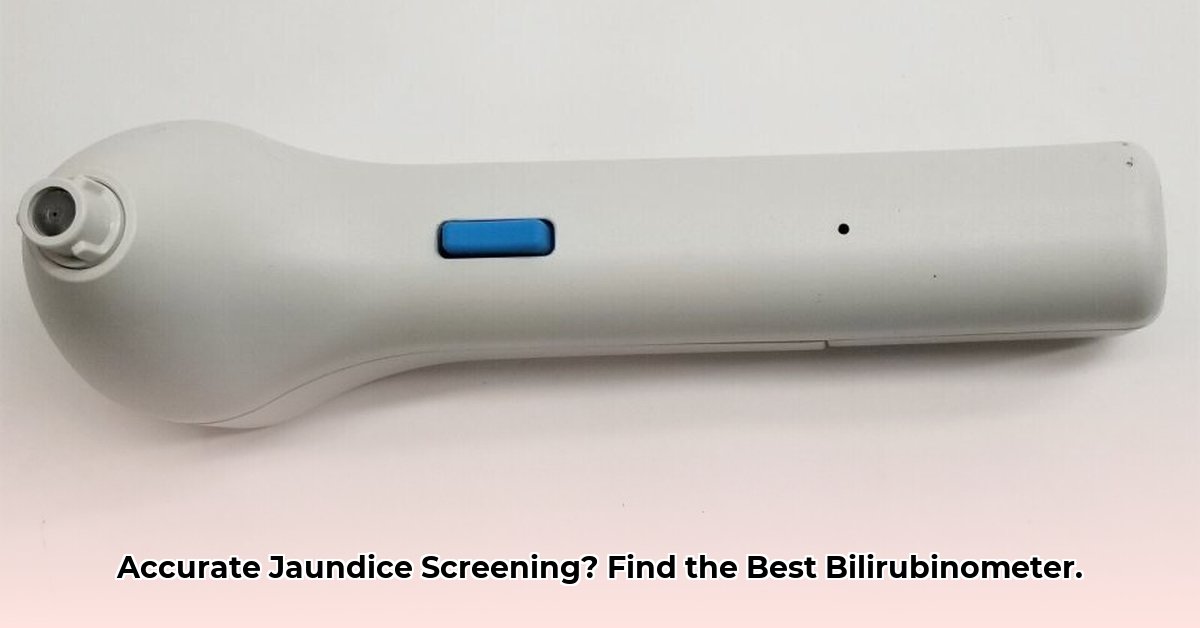
Picking the right machine to measure bilirubin levels in newborns is a big deal for hospitals. Getting accurate readings quickly is essential for treating jaundice, and this guide will help you understand the choices. We’ll compare two main types of bilirubinometers – those that measure bilirubin through the skin (transcutaneous) and those that need a blood sample (serum). We’ll weigh the pros and cons of each, helping you decide what’s best for your hospital. We’ll also cover how to use these machines effectively, save money, and make sure your hospital stays up-to-date with the latest technology in newborn care. For a deeper dive into TcB vs. serum bilirubin, see this helpful resource: TcB vs Serum.
Bilirubinometer Selection for Hospitals: Optimizing Neonatal Jaundice Screening Programs
Choosing the right bilirubinometer is crucial for any hospital’s newborn care unit to optimize neonatal jaundice screening programs. These devices quickly and accurately measure bilirubin levels in babies, helping doctors and nurses spot and treat jaundice efficiently. Untreated jaundice can be serious, so getting the right diagnosis fast is a big deal. This article explores the available options, helps you make the best choice for your hospital, and explains how to optimize its use, ensuring effective neonatal jaundice management and accurate bilirubin screening.
Understanding the Importance of Speedy and Accurate Jaundice Detection
Newborn jaundice is common; however, it requires prompt detection and accurate assessment. It’s a condition where there’s a buildup of bilirubin, a yellowish pigment, in a baby’s blood. While often mild and easily treated, untreated jaundice can, in some cases, lead to serious health problems. That’s why fast and accurate detection is a top priority. Bilirubinometers are the tools that allow healthcare professionals to do this. They give a quick assessment, guiding them on whether further tests or treatment are needed, emphasizing the importance of early jaundice detection and monitoring neonatal bilirubin levels. Delays in diagnosis can lead to increased hospital stays and potential complications.
Two Main Ways to Measure Bilirubin: Transcutaneous vs. Serum
Hospitals use two main methods to measure bilirubin: transcutaneous (TcB) and serum bilirubin measurement (TSB). Think of it this way: TcB is a non-invasive method, like taking a baby’s temperature – quick and easy. A special sensor gently touches the baby’s skin, typically on the sternum or forehead, to measure bilirubin levels. It’s super convenient for initial screenings and getting quick results. Serum tests, on the other hand, require a small blood sample obtained via heel stick. While slightly more invasive, a serum test provides a direct and highly precise measurement of bilirubin levels. Many hospitals use both methods – TcB for initial quick checks, followed by a serum test for confirmation or when TcB levels exceed a certain threshold. This combined approach provides a comprehensive picture of transcutaneous bilirubin testing and serum bilirubin analysis. Note that factors like skin pigmentation, gestational age, and the specific device used can influence TcB accuracy.
Choosing the Best Bilirubinometer: Factors to Consider
Picking the right bilirubinometer for your hospital involves several key factors:
-
Accuracy & Precision: How precise are the measurements? Even a small mistake can affect the baby’s treatment. Look for devices with good correlation to serum bilirubin measurements and consider the clinical context when interpreting results. You want a device that delivers reliable results, ensuring accurate jaundice diagnosis.
-
Ease of Use: Ease of use is critical. The device should be intuitive and easy to operate, especially during busy shifts. A simple, straightforward design minimizes the chance of operator error, emphasizing user-friendly medical devices. Training should be readily available and easy to understand.
-
Portability: Some hospitals might need portable devices for bedside testing or quick screenings in different areas of the hospital. Others might prefer a stationary unit in the lab. Your hospital’s needs will dictate this choice, determining the need for portable bilirubinometers. Consider the device’s weight and battery life if portability is a priority.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Balancing the cost of the device with its features and long-term functionality is essential. Consider initial purchase price, disposable costs (if applicable), and potential service contracts. Some devices may have lower initial costs but higher running costs due to disposable materials, highlighting the importance of cost-effective medical equipment.
-
Maintenance Requirements: Regular maintenance is necessary to keep your bilirubinometer running efficiently and giving reliable results. A simple, straightforward maintenance routine is a big plus, focusing on bilirubinometer maintenance. Determine the frequency of required calibrations and the ease of performing these tasks.
-
Data Management & Connectivity: Seamless integration with your hospital’s existing systems (like electronic health records) simplifies data management and helps create a comprehensive patient record, emphasizing EHR integration and hospital information systems. Consider devices with wireless connectivity and data storage capabilities.
-
Flagging Capabilities: Some devices offer integrated flagging features to help keep track of patients in need of special attention, assisting in compliance with jaundice management protocols.
Comparing Leading Bilirubinometer Models: A Quick Overview
The table below offers a simplified comparison of key features. Keep in mind that specific specifications vary depending on the manufacturer and model. Always check the manufacturer’s details for the most accurate information.
| Feature | Transcutaneous Bilirubinometer (TcB) | Serum Bilirubinometer |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Method | Non-invasive, skin sensor | Invasive, blood sample |
| Speed | Very fast, immediate or near-immediate results | Slower, requires lab processing |
| Accuracy | Generally good for screening, may need further testing | High accuracy, often considered the gold standard |
| Cost | Typically lower initial investment | Higher initial cost, often requires additional supplies |
| Portability | Often portable and easily moved | Usually stationary, located in the lab |
| Maintenance | Relatively simple | Can be more complex, depending on the equipment |
| Sample Required | None | Small blood sample |
| Pain/Discomfort | None | Minimal, associated with heel stick |
Implementing a Bilirubinometer in Your Hospital Workflow: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Needs Assessment: Start by carefully evaluating your hospital’s specific needs. Consider the number of newborns, existing resources, workflow requirements, and budget constraints.
- Device Selection: Choose a bilirubinometer that perfectly meets your criteria. This includes factors like accuracy, ease of use, cost, portability, and data management capabilities, aligning with hospital equipment procurement.
- Staff Training: Make sure your staff receive thorough training on the device’s operation, maintenance, and any safety procedures. Proper training ensures accurate results and device longevity, emphasizing medical device training. Include competency assessments as part of the training program.
- Protocol Development: Establish clear protocols for jaundice screening, including when to use TcB, when to obtain a serum bilirubin level, and treatment thresholds.
- Integration into Workflow: Carefully integrate the device into your existing workflow to ensure smooth operation and efficient use of staff time. Consider the location of the device and the availability of trained personnel.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustment: Regularly monitor the device’s performance and make adjustments to your workflow as needed. This ensures that you’re getting the most out of your investment, and providing the best possible patient care. This includes tracking the number of TcB measurements performed, the number of serum bilirubin levels ordered, and the number of infants requiring treatment for jaundice.
- Quality Assurance: Implement a quality assurance program to regularly check the accuracy and reliability of the bilirubinometer. This may involve comparing TcB results with serum bilirubin levels.
The Future of Neonatal Jaundice Screening: What’s on the Horizon?
The technology behind neonatal jaundice screening is constantly evolving. We can likely expect to see more sophisticated devices in the near future, offering even greater accuracy, speed, and easier use. This includes advancements in sensor technology, algorithms, and integration with other hospital systems. Artificial intelligence is likely to play an increasingly important role, further improving the speed and accuracy of diagnosis, highlighting innovative jaundice screening and AI in healthcare. Telemedicine applications may also become more prevalent, allowing for remote monitoring of bilirubin levels.
Cost Savings and Efficiencies with Bilirubinometers
Bilirubinometers streamline jaundice screening practices by reducing time-consuming blood draws, scheduling of laboratory work, and processing costs. They improve efficiency by delivering reliable measurements with significantly fewer steps, freeing up more time for direct infant care. Transcutaneous bilirubinometers, in particular, reduce the need for painful and potentially traumatic heel sticks, leading to improved patient and parental satisfaction. The data transfer functionality and barcode scanners help you optimize your screening program and reduce the risk of human error. Some devices have reusable probe tips, eliminating the need for disposables. With the volume of screenings performed in nurseries today, the cost of disposable items can ultimately exceed the initial cost of the device itself. As a result, you save time and money while delivering an exceptional standard of care.
Choosing the right bilirubinometer is a critical decision for hospitals. It’s an investment in providing high-quality care to newborns. By carefully considering the factors discussed above, hospitals can select a device that optimizes their jaundice screening processes, ensuring optimal neonatal care.
- How To Create Free Electricity Using Home Renewable Sources - January 30, 2026
- How to Produce Electricity at Home for Energy Independence - January 29, 2026
- How To Create Electricity At Home For Energy Independence - January 28, 2026